As we approach World Environment Day 2019, many organizations are considering how they might want to acknowledge and celebrate their environmental initiatives. The Earth Day Network for years has encouraged businesses and consumers to commit to acts of green, which involve making more sustainable choices, and they have currently reached 2.68 billion acts! These acts usually involve an event, making a pledge, organizing volunteer work, or even breaking a Guinness World Record (or maybe that was just Sims Recycling Solutions in 2012 and 2013).
Whatever the initiative, every company plays a role in contributing to sustainable and circular economy initiatives with the goal of helping preserve our environment. This can even benefit corporations when they choose to present their efforts in corporate sustainability reports at the end of the year.
There are many reasons why secure and responsible e-Recycling is important to embrace. Here is a breakdown of four main reasons why every company should take their e-waste recycling efforts seriously.
1. To Preserve our Planet
This is an obvious reason, but is still important enough to mention. Reusing commodities retrieved from retired electronics is often referred to as “urban mining” and avoids the need to mine further raw materials. This can be a great way to,
- Sustain the life of these finite resources,
- Avoid raw material mining, and
- Prevent them from being disposed of in landfills.
Electronic waste contains harmful materials which include brominated flame retardants, cadmium, chromium, lead and mercury. If these devices are not responsibly disposed of, where do they go? If they end up sitting in a landfill, those hazardous components can leach into our soil, water and food.
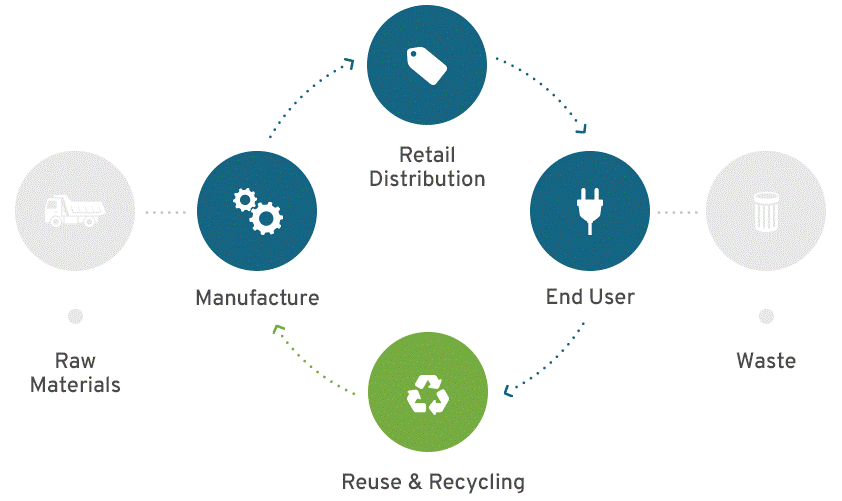
There are many organizations fighting this issue and making great headway, but we have a long way to go. In a traditional linear materials model, products are manufactured from raw materials, sold and distributed to consumers, and most likely landfilled once items are no longer in use.
Today we are moving more significantly toward a circular economy structure with leading OEMs managing the full lifecycle of their products. This allows used recyclable materials to be part of the design process. Manufactured materials are basically retrieved from the marketplace and sent back to the manufacturer to be used again. This model is possible and is happening today with leading OEMs, but will take more cooperation between manufacturers, recyclers, governments and consumers to be implemented across the board.
2. Maintain Brand Reputation
There are two main ways improper e-waste disposal can result in reputational damage to a brand. From a security standpoint, if a bad recycler dumps company-owned equipment, not only is the company liable but it could put them at risk of a data disaster. As we have all seen, a data breach can cause distrust in consumers and/or clients. Environmentally, if equipment is improperly disposed of and it is tracked back to a business, it sends the message that they are contributing to the problem of global e-waste dumping.
Data Security
Most electronic hardware manufactured today is made up of a large amount of materials and components, and most likely stores some level of data. When disposed of we all need to consider data stored on these devices, and reuse of materials the device is made of.
Data security has been a major focus over the last few years, as Gemalto revealed just in 2018 there were 945 data breaches that lead to 4.5 billion data records being compromised. When suffering a data breach companies have to deal with financial damage, which recently increased by more than six percent last year costing an average of $3.86 million per breach. There are also hidden costs however, that can involve loss of business and distrust of clients.
Environmental Liability
Aside from data security, environmental liability can also be damaging if equipment ends up being illegally dumped. Depending on a company’s location, they could be held liable for the e-waste dumping and suffer the consequences. Ensuring all IT assets and waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) are managed responsibly can demonstrate a company’s commitment to doing what is right.
3. Maximize Recovery Value
E-Recycling does not always have to involve the end-of-life processing. One of the best ways to sustain the life cycle of devices, is to reuse units or parts until they no longer function. Reuse and resale of equipment is not only sustainable and environmentally friendly, but it maximizes the value of the device as well, and can become an additional revenue stream for companies.
If you do not already have an asset recovery strategy, there are a few options for doing so:
- Resell items through wholesale and retail channels
- Redeploy devices back into your business
- Recover parts and components for reuse
- Responsibly recycle the items that no longer have a useful life
Some recyclers can include this in their recycling suite of services. However it can really make a difference if the recycler is experienced in IT resale, and can utilize their skillset to maximize the return for clients.
4. Avoid Grey Market Distribution
Oftentimes, manufacturers will send their electronics recycler items they want taken off the market. Whether they have a new prototype they don’t want released or they came out with a new product, there are circumstances where e-Recyclers are handed devices that are still in working condition, but sent for end-of-life recycling.
The term “grey market” describes the situation where a product is sold through a legal, but unauthorized channel. There have been issues of products sent for destruction and recycling only to find recyclers selling them on the side without permission.
Especially for original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), it is critical to maintain product placement and value, as well as compliance. When innovating and testing new products, keeping prototypes secure is critical for a successful product launch and to keep a competitive advantage. OEMs must be conscious of who their recycler is and how they will responsibly recycle their electronic products.
With 20-50 million metric tons of e-waste around the world disposed of annually, every company should ensure they have a process for managing their retired or replaced electronics to optimize material recovery and minimize impact.
This Earth Day, learn more about developing sustainable partnerships that can optimize material recycling and minimize environmental impact.